

- Hexa His tag peptide
- 3X FLAG Peptide
- T7 Tag Peptide
- FLAG tag Peptide
| S Tag PeptidePancreatic RNase A derivtive |

Sample solution is provided at 25 µL, 10mM.
 Nature.2017 Jan 19;541(7637):417-420.
Nature.2017 Jan 19;541(7637):417-420. Nature.2018 Nov;563(7731):407-411.
Nature.2018 Nov;563(7731):407-411. Nature.2018 Jun 13.
Nature.2018 Jun 13. Nature.2018 Jun 27.
Nature.2018 Jun 27. Nature.2018 Mar 29;555(7698):673-677.
Nature.2018 Mar 29;555(7698):673-677. Nature.2017 Sep 7;549(7670):96-100.
Nature.2017 Sep 7;549(7670):96-100. Nature.2016 Apr 21;532(7599):398-401.
Nature.2016 Apr 21;532(7599):398-401. Science.2016 Aug 5;353(6299)594-8
Science.2016 Aug 5;353(6299)594-8 Nat Nanotechnol.2017 Dec;12(12):1190-1198.
Nat Nanotechnol.2017 Dec;12(12):1190-1198. Nature Biotechnology.2017 Jun;35(6):569-576
Nature Biotechnology.2017 Jun;35(6):569-576 Nat Med.2018 Sep 17.
Nat Med.2018 Sep 17. Cell.2018 Dec 21. pii: S0092-8674(18)31561-7.
Cell.2018 Dec 21. pii: S0092-8674(18)31561-7. Cell.Available online 25 October 2018.
Cell.Available online 25 October 2018. Cell.2018 Sep 27. pii: S0092-8674(18)31183-8.
Cell.2018 Sep 27. pii: S0092-8674(18)31183-8. Cell.2018 Jun 28;174(1):172-186.e21.
Cell.2018 Jun 28;174(1):172-186.e21. Cell.2018 Feb 22;172(5):1007-1021.e17.
Cell.2018 Feb 22;172(5):1007-1021.e17. Cell.2017 Nov 30;171(6):1284-1300.e21.
Cell.2017 Nov 30;171(6):1284-1300.e21. Cell.2017 Aug 17. pii: S0092-8674(17)30869-3.
Cell.2017 Aug 17. pii: S0092-8674(17)30869-3. Cell.2017 Jul 13;170(2):312-323
Cell.2017 Jul 13;170(2):312-323 Nat Med.2018 Jan 29.
Nat Med.2018 Jan 29. Nat Med.2017 Nov;23(11):1342-1351.
Nat Med.2017 Nov;23(11):1342-1351. Cell.2017 Apr 6;169(2):286-300.
Cell.2017 Apr 6;169(2):286-300. Cell.2015 Aug 27;162(5):987-1002.
Cell.2015 Aug 27;162(5):987-1002. Cell.2015 Feb 12;160(4):729-44.
Cell.2015 Feb 12;160(4):729-44. Nature Medicine.2017 Apr;23(4):493-500.
Nature Medicine.2017 Apr;23(4):493-500. Cancer Cell.2018 May 14;33(5):905-921.e5.
Cancer Cell.2018 May 14;33(5):905-921.e5. Cancer Cell.2018 Apr 9;33(4):752-769.e8.
Cancer Cell.2018 Apr 9;33(4):752-769.e8. Cancer Cell.2018 Mar 12;33(3):401-416.e8.
Cancer Cell.2018 Mar 12;33(3):401-416.e8. Cancer Cell.2017 Aug 14;32(2):253-267.e5.
Cancer Cell.2017 Aug 14;32(2):253-267.e5. Nat Methods.2018 Jul;15(7):523-526.
Nat Methods.2018 Jul;15(7):523-526. Cell Stem Cell.2018 May 3;22(5):769-778.e4.
Cell Stem Cell.2018 May 3;22(5):769-778.e4. Cell Stem Cell.2017 Nov 20. pii: S1934-5909(17)30375-2.
Cell Stem Cell.2017 Nov 20. pii: S1934-5909(17)30375-2.Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
- Purity = 96.56%
- COA (Certificate Of Analysis)
- HPLC
- MS (Mass Spectrometry)
- MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet)
- Datasheet
Chemical structure
| Description | S Tag Peptide is an oligopeptide derived from pancreatic ribonuclease A used for improving protein solubility. | |||||
| Targets | anti-S-Tag antibody | |||||
| IC50 | ||||||

S Tag Peptide Dilution Calculator
calculate

S Tag Peptide Molarity Calculator
calculate
| Cas No. | SDF | Download SDF | |
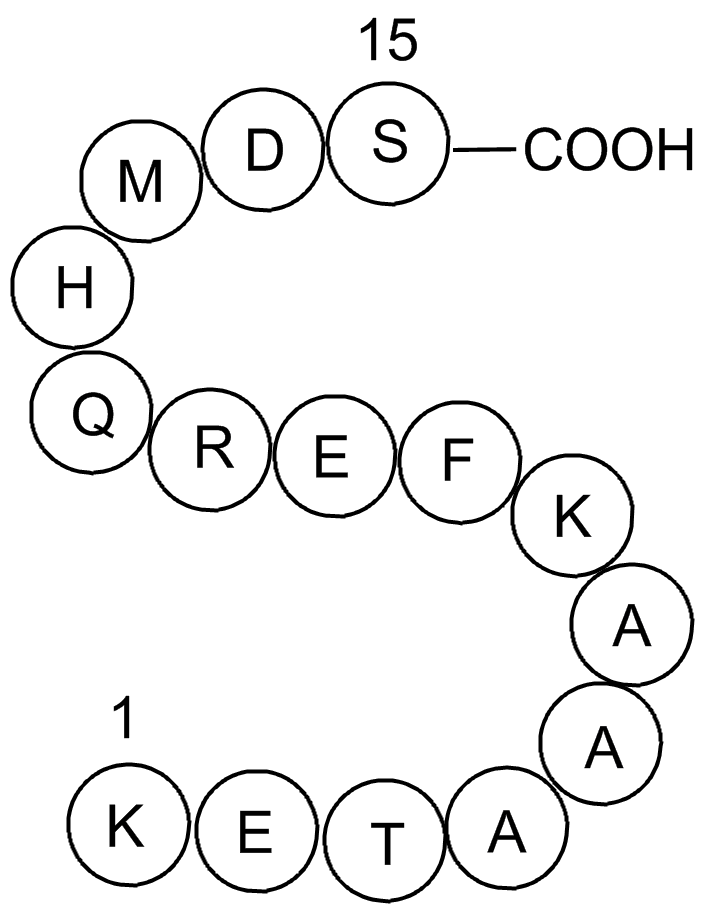
| Synonyms | H-Lys-Glu-Thr-Ala-Ala-Ala-Lys-Phe-Glu-Arg-Gln-His-Met-Asp-Ser-OH | ||
| Chemical Name | S Tag | ||
| Canonical SMILES | CC(C(C(=O)NC(C)C(=O)NC(C)C(=O)NC(C)C(=O)NC(CCCCN)C(=O)NC(CC1=CC=CC=C1)C(=O)NC(CCC(=O)O)C(=O)NC(CCCNC(=N)N)C(=O)NC(CCC(=O)N)C(=O)NC(CC2=CN=CN2)C(=O)NC(CCSC)C(=O)NC(CC(=O)O)C(=O)NC(CO)C(=O)O)NC(=O)C(CCC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(CCCCN)N)O | ||
| Formula | C73H117N23O25S | M.Wt | 1748.91 |
| Solubility | ≥174.9mg/mL in DMSO | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Physical Appearance | A solid | Shipping Condition | Evaluation sample solution : ship with blue ice.All other available size:ship with RT , or blue ice upon request |
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. | ||
S Tag is the name of an oligopeptide derived from pancreatic ribonuclease A (RNase A). If RNase A is digested with subtilisin, a single peptide bond is cleaved, but the resulting two products remain weakly bound to each other and the protein, it is called ribonuclease S, remains active although each of the two products alone shows no enzymatic activity. The N-terminus of the original RNase A, also called S-peptide, consists of 20 amino acid residues, of which only the first 15 are required for ribonuclease activity. This 15 amino acids long peptide is called S15 or S-tag.
It is believed that the peptide with its abundance of charged and polar residues could improve solubility of proteins it is attached to. Moreover, the peptide alone is thought not to fold into a distinct structure. On DNA-level the S-tag can be attached to the N- or C-terminus of any protein. After gene expression, such a tagged protein can be detected by commercially available antibodies. [1]
References: 1.R.T. Raines et al., The S-Tag Fusion System for Protein Purification. Methods Enzymol. 326, 362-367 (2000)




