
- 转铁蛋白和apotranferrins
- Lab Reagents: Smart Buffers and Reagents
- 分子生物学用酶:分子生物学用酶
- 蛋白质纯化:阿波罗20毫升超滤
- 免疫球蛋白
- qPCR:基因分析和基因面板
- PCR : PCR Products
- 牛奶和血小板蛋白
- DNA & RNA Sequencing : Dye Terminator clean-up
- Aptamers: Catalogue Aptamers
- Peptide Synthesis : Amino Acids
- 运输和其他蛋白质
- DNA: Whole DNA
- STEM学习:STEM工具包
- 低内毒素水平蛋白质
- 提取和纯化-RNA:组织/培养
- 转染-EZ生物系统:细胞系
- 凝血因子
- 分析试剂盒
- 抗体
- Gel Electrophoresis: Gel Electrophoresis


STEM Learning: STEM Kits
A range of easy to use kits for PCR, gel electrophoresis and other molecular biology techniques especially designed for budding school students, in schools, 6th form colleges and other educational institutes.
miniPCR™ Forensics Lab-Analysis of the D1S80 VNTR
n this miniPCR Learning Lab™, students will amplify their own DNA and compare it to a sample obtained from a hypothetical crime scene in order to try to rule themselves out as a suspect. Students will use essential molecular biology techniques of PCR (polymerase chain reaction), gel electrophoresis, and VNTR (variable number tandem repeat) analysis. This lab illustrates real-world applications of molecular biology in personal identification and forensics and in the study of inheritance, human genetics, DNA polymorphisms, and genetic diversity.- A REALISTIC CRIME SCENE INVESTIGATION.
MiniPCR - Amplyus
| Catalogue No. | Description | Pack Size | Price | Qty |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MP-KT-1009-01 | miniPCR™ Forensics Lab: Analysis of the D1S80 VNTR | each | £76.00 | Quantity | Add to Order |
miniPCR™ Forensics Lab-Analysis of the D1S80 VNTR
n this miniPCR Learning Lab™, students will amplify their own DNA and compare it to a sample obtained from a hypothetical crime scene in order to try to rule themselves out as a suspect. Students will use essential molecular biology techniques of PCR (polymerase chain reaction), gel electrophoresis, and VNTR (variable number tandem repeat) analysis. This lab illustrates real-world applications of molecular biology in personal identification and forensics and in the study of inheritance, human genetics, DNA polymorphisms, and genetic diversity.- A REALISTIC CRIME SCENE INVESTIGATION.
MiniPCR - Amplyus
In this miniPCR Learning Lab™, students will amplify their own DNA and compare it to a sample obtained from a hypothetical crime scene in order to try to rule themselves out as a suspect. Students will use essential molecular biology techniques of PCR (polymerase chain reaction), gel electrophoresis, and VNTR (variable number tandem repeat) analysis. This lab illustrates real-world applications of molecular biology in personal identification and forensics and in the study of inheritance, human genetics, DNA polymorphisms, and genetic diversity.


A REALISTIC CRIME SCENE INVESTIGATION.
In this miniPCR Learning Lab™, students will amplify their own DNA and compare it to a sample obtained from a hypothetical crime scene in order to try to rule themselves out as a suspect. Students will use essential molecular biology techniques of PCR (polymerase chain reaction), gel electrophoresis, and VNTR (variable number tandem repeat) analysis. This lab illustrates real-world applications of molecular biology in personal identification and forensics and in the study of inheritance, human genetics, DNA polymorphisms, and genetic diversity.
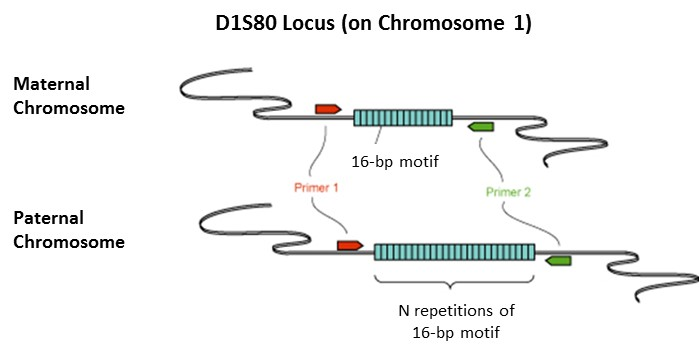
Variable number tandem repeats (VNTRs) are regions in a genome that contain short stretches of DNA (6 to about 100 base pairs) repeated a number of times. The number of repeats in a particular VNTR can vary from individual to individual, and between chromosomes within an individual. In this way, VNTRs are one source of genetic polymorphism (variation), and can be used as markers for personal identification as well as in the study of inheritance, genetic diversity, population genetics, and genetic disorders.
This lab is presented as a hypothetical crime where DNA evidence has been collected. Included in the lab is a sample of “Crime Scene DNA” that will be used by students to compare to their own DNA sample. Students whose DNA does not match the “Crime Scene DNA” can rule themselves out as suspects. It is possible that some students will match the DNA sample provided. These students cannot rule themselves out and are considered possible suspects.
This Learning Lab is aligned with National Standards. It utilizes the following molecular genetic techniques:
- DNA extraction from cheek cells
- PCR amplification of human genomic DNA
- DNA Gel electrophoresis, staining, and visualization
- VNTR (variable tandem number repeat) analysis
The miniPCR Forensics Lab kit contains reagents for 8 lab groups of 4 students each (32 students):
- X-Tract™DNA extraction buffer
- 2X Blue PCR Master Mix, Load-Ready™
- D1S80 Lab Primer Mix
- “Crime Scene” DNA control sample
- 100 bp DNA ladder, Load Ready™
Please note:
- These reagents require frozen storage.
- Microtubes,PCR tubes, and electrophoresis reagents sold separately(or select the option above for Lab Companion Kitadd-on)
Free miniPCR Learning Lab™downloads:
- miniPCR Forensics Lab Instructor’s Guide
- miniPCR Forensics Lab Student’s Guide
- miniPCR Forensics Lab Classroom Slides
- D1S80 Data Spreadsheet
- Case Study: miniPCR use in real-world forensics
- DNAdots: DNA Fingerprinting
If you cannot find the answer to your problem below then please contact us or telephone 01954 210 200




 Description
Description